AVC
This is by far the most popular video codec. AVC has relatively fast encoding speed and can support videos up to 3840x2160 in resolution.
Hardware encoding support is available for AVC and can be enabled using the Hardware checkbox in the AVC > Main tab. Scroll down this page for more details. The supported hardware encoders are: NVENC (Nvidia), QuickSync (Intel), or AMF (AMD).
Recommend for:
General purpose, fast yet high quality encode, videos intended to be shared online, universal support across all devices.
NOT recommend for:
Resolutions above 3840x2160, high compression, videos with more than 8-bit color depth.
Usage
Encoding Mode
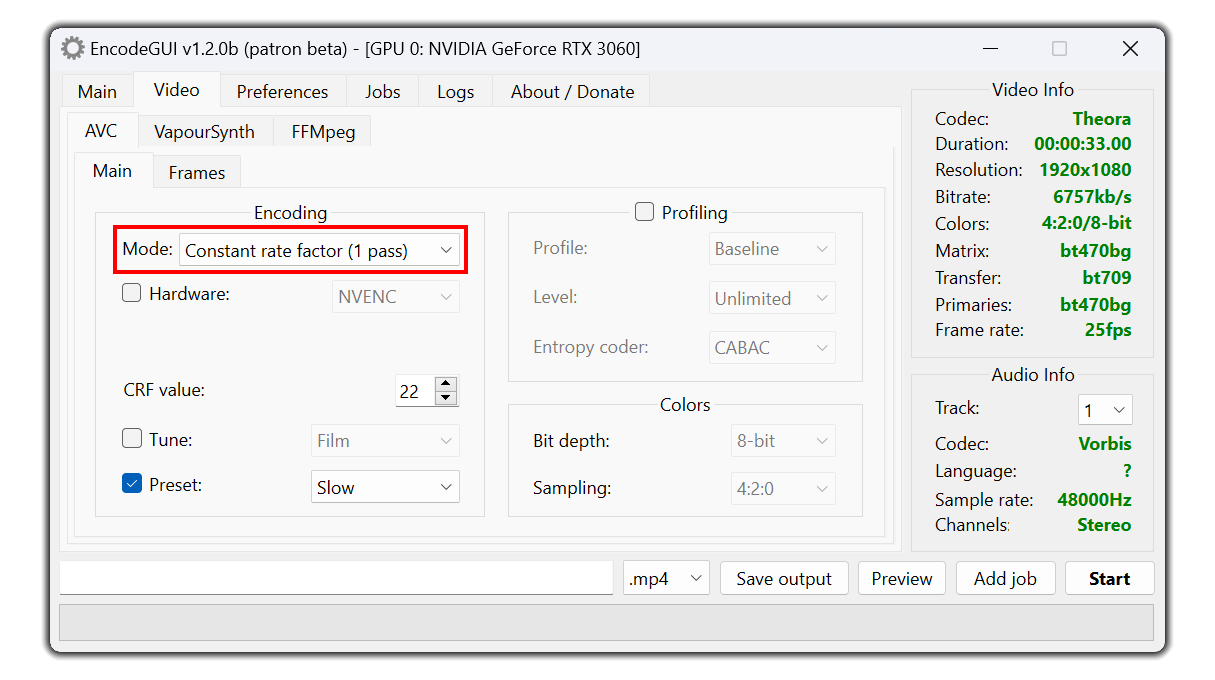
This is the recommended option. The video bitrate is automatically adjusted during the encoding process in accordance with the CRF value to provide a high quality output while having a highly compressed video.
Lower values = better quality (min: 0).
Higher value = lower quality (max: 51).
Lossless quality = 0.
Recommend option = 17.
Average Bitrate (1 pass):
Encodes the video in a defined average bitrate (kbits/s). The required bitrate varies on the basis of the resolution of the video, the frame rate, and the colors.
Higher value = higher quality.
Lower value = lower quality.
Target Bitrate (2 pass):
Encodes the video to a specified file size or a specific bitrate. This option is recommended if you need the video file to be at a specific file size. This encoding method is 2 pass, meaning the video encodes twice.
Constant Quantizer (1 pass):
This option is similar to Constant Rate Factor, but does not consider the visual aspects when encoding the video like Constant Rate Factor. This is the next best alternative to Constant Rate Factor rate control.
Lower values = better quality (min: 0).
Higher value = lower quality (max: 51).
Lossless quality = 0.
Recommend option = 17.
Hardware Encoding
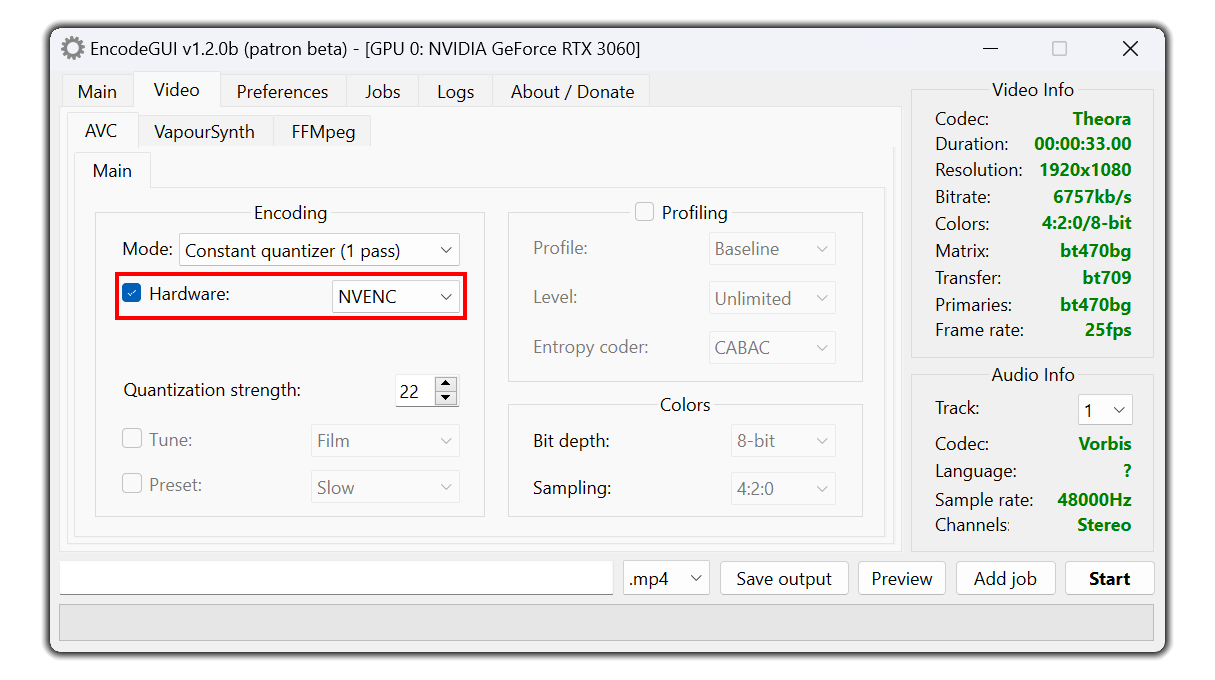
Note: Hardware encoding isn’t recommended to use because it does not produce the same high quality output that the software encoding counterpart has.
NVENC:
This hardware encoder utilizes Nvidia GPUs.
Constant quantizer, Average bitrate, and Target bitrate are all supported rate controls.QuickSync:
This hardware encoder utilizes Intel GPUs.
Constant quantizer, Average bitrate, and Target bitrate are all supported rate controls.AMF:
This hardware encoder utilizes AMD GPUs.
Constant quantizer, Average bitrate, and Target bitrate are all supported rate controls.Profile and Tune:
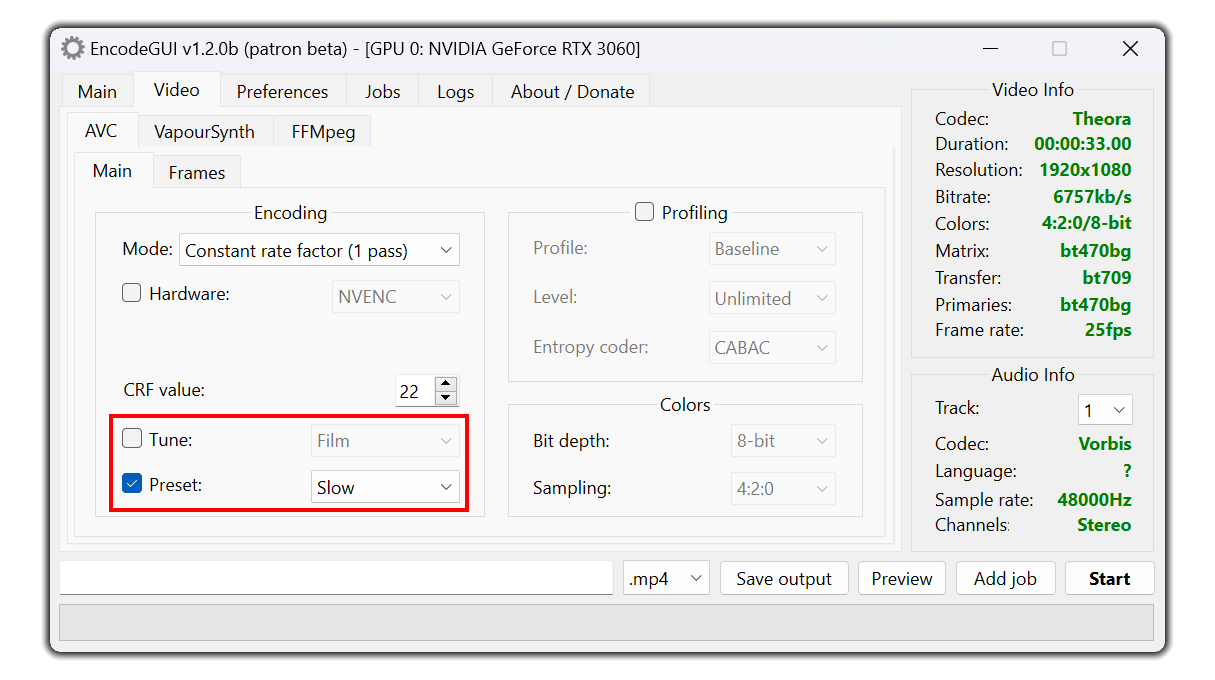
Sets the tune for the video on the basis of what type of video the source is.
Preset:
Sets the CPU preset (speed) to use for encoding.
Higher preset = faster encode but lower quality.
Lower preset = slower encode but higher quality.
Recommended: slow
AVC Profiling
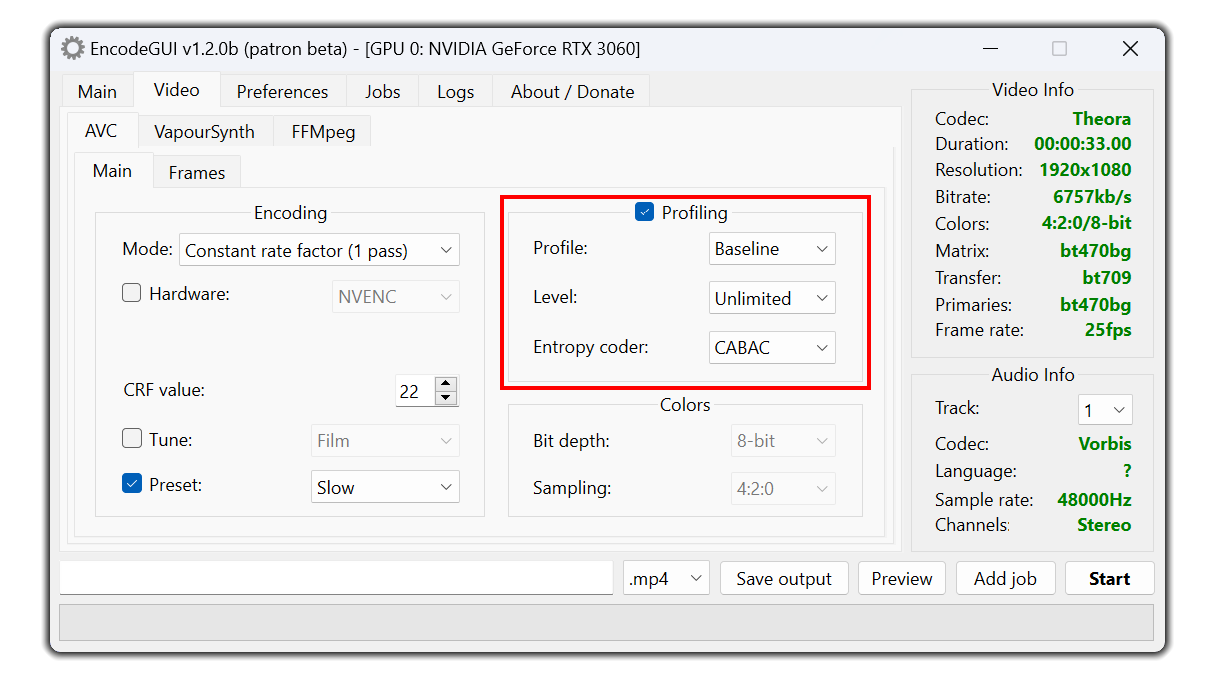
Profile:
The encoding profile to use. The recommended option to use is
High for most videos. Select High 10 for videos in 10-bit color depth and adjust the color depth in the colors group box to 10-bit. For videos in 4:2:2 sampling, set the profile to High 4:2:2 and set the color sampling to 4:2:2 in the colors group box.Level:
The level to assign to the video profile. This option should be set on the basis of the resolution and frame rate of the video. Use a higher level for high frame rate / resolution videos and use a lower value for low frame rate / resolution videos. Set to
Unlimited to allow the encoder to automatically assign a level (recommended).Frames
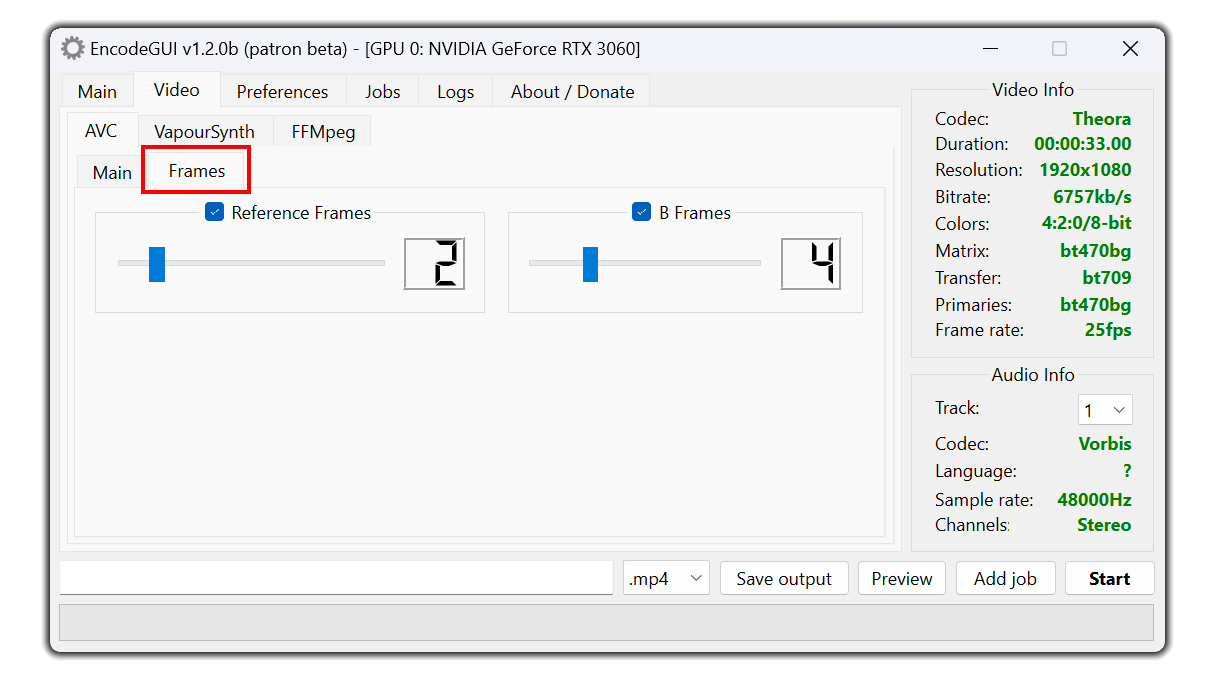
The number of reference (future) frames for the encoder to use.
B-Frames:
The number of B-frames/prediction frames to assign to the video. More B-frames typically allow higher video compression.